WEEK 2 | Home Task
Information Diagram
From light to vision: The process of seeing with the human eye.
Research:
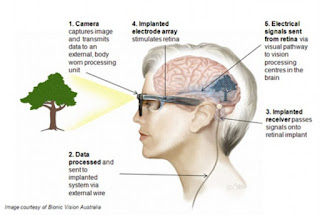
Light rays enter the eye
through the cornea, the clear front “window” of the eye. The cornea’s
refractive power bends the light rays in such a way that they pass freely
through the pupil the opening in the center of the iris through which light
enters the eye.
The iris works like a shutter
in a camera. It has the ability to enlarge and shrink, depending on how much
light is entering the eye.
After passing through the iris,
the light rays pass through the eye’s natural crystalline lens. This clear,
flexible structure works like the lens in a camera, shortening and lengthening
its width in order to focus light rays properly.
Light rays pass through a
dense, transparent gel-like substance, called the vitreous that fills the globe
of the eyeball and helps the eye hold its spherical shape.
In a normal eye, the light rays
come to a sharp focusing point on the retina. The retina functions much like
the film in a camera. It is responsible for capturing all of the light rays,
processing them into light impulses through millions of tiny nerve endings,
then sending these light impulses through over a million nerve fibers to the
optic nerve.
Because the keratoconus cornea
is irregular and cone shaped, light rays enter the eye at different angles, and
do not focus on one point the retina, but on many different points causing a
blurred, distorted image.
In summary, the cornea is the
clear, transparent front covering which admits light and begins the refractive
process. It also keeps foreign particles from entering the eye.The pupil is an adjustable
opening that controls the intensity of light permitted to strike the lens. The
lens focuses light through the vitreous humor, a clear gel-like substance that
fills the back of the eye and supports the retina.
The retina receives the image
that the cornea focuses through the eye’s internal lens and transforms this
image into electrical impulses that are carried by the optic nerve to the
brain. We can tolerate very large scars on our bodies with no concern except
for our vanity. This is not so in the cornea. Even a minor scar or irregularity
in the shape can impair vision. No matter how well the rest of the eye is
functioning, if the cornea is scarred, clouded or distorted, vision will be
affected.In keratoconus, the irregular
shape of the cornea does not allow it to do its job correctly, leading to
distortion of the image it passed to the retina and transmitted to the brain.


Step 1:
Light rays pass through the eye’s clear front cover called the cornea.
Step 2:
Light passes through the eyes pupil, the eye’s window to the world. The pupil is surrounded by a sphincter call the iris; the eye’s colored ring.
Step 3:
Light passes through the eye’s crystalline lens, which constricts to help light rays come to focus at one focal point.
Step 4:
Light rays travel to and come to rest on the retina resulting in clear vision.
Step 5:
Once light rays come to rest on the retina a signal is carried done the optic nerve to the brain.
Step 6:
The brain receives the signals and interprets them into a picture(s).
Step7:
The brain tells the eyes what it sees by forming the picture.
Sources:
Sketches:
Final piece:
Non-descriptive: works better with an article
Descriptive: would work as a stand-alone piece






Comments
Post a Comment